-
Solar Impulse 2 lands at Seville airport, Spain.Getty Images
-
The Spanish Air Force "Patrulla Aguila" (their Red Arrows essentially) performing just before Solar Impulse 2 landed in Seville this morning.Getty Images
-
Solar Impulse 2 test flight
-
Solar Impulse 2, taking off from Nanjing, China, towards Hawaii
-
-
Solar Impulse 2, arriving in Abu Dhabi
-
Solar Impulse 2, arriving in Abu Dhabi
-
A wingspan comparison between a 747 and Solar Impulse 2
-
Solar panels!!
-
-
André Borschberg, in the cockpit of Solar Impulse 2, just after arriving in Oman
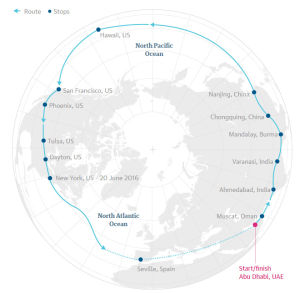
Solar Impulse 2 has landed in Seville, completing the world's first solar-powered crossing of the Atlantic. The 6765km (4,200mi) flight took just shy of three days (71 hours and 8 minutes), taking off from New York three days ago.
Solar Impulse 2, which is slowly making its way back around the world to Abu Dhabi, has two pilots that take turns. The Atlantic hop was Bertrand Piccard's longest flight in Solar Impulse 2. André Borschberg, who piloted the agonisingly drawn-out Nagoya-to-Hawaii leg, still retains the record for longest ever solo flight (8924km over 117 hours and 52 minutes) back in July 2015.
The flights take such a long time because Solar Impulse 2, as the name suggests, is completely powered by sunlight. The plane's massive 72-metre wings (broader than a 747!) are covered in some 269.5 square metres of photovoltaic cells. During the day, the cells power four 14kW (17.4hp) electric motors and top-up four 41kWh lithium-ion batteries. During the evening, the motors are driven by the batteries. Max cruise speed when the sun is up is 49 knots (90km/h), and a rather languid 33 knots (60km/h) at night.
The solar cells don't quite refill the batteries during the day, which means the plane can't fly forever just yet. Max flight duration is somewhere around five to six days.
For power-saving reasons, the Solar Impulse 2 cockpit can only carry a single human, and is both unheated and unpressurised. The pilots do sleep while they're up in the air, but usually just for 20 minutes at a time (the telemetry data for one flight showed 10 catnaps of 20 minutes over a 24-hour period). Now multiply those conditions by a continuous flight time of three or four days and you have some idea of the rigours that Piccard and Borschberg must go through.
Talking to the Guardian this morning, while still a few hours out from Seville, Piccard spoke about the significance of a solar-powered crossing of the Atlantic. “The Atlantic is the symbolic part of the flight," he said. "It is symbolic because all the means of transportation have always tried to cross the Atlantic, the first steamboats, the first aeroplane, the first balloons, the first airships and, today, it is the first solar-powered aeroplane.
"But the goal is not to change aviation, as Charles Lindbergh did, but to inspire people to use [renewable] technologies and show people they can use these technologies every day to have a better quality of life."
Solar Impulse 2 now, in theory, only has one flight left to complete its circumnavigation of the globe: from Seville to Abu Dhabi. We don't know when the flight will be (it depends on weather conditions and the state of the aircraft), but we'll certainly bring you some updates when it happens.
Listing image by Solar Impulse
reader comments
46